The COVID-19 pandemic has made clear that the Internet plays a critical role in society, and it’s underlined the importance of reliable Internet connectivity for everyone. It’s also highlighted a stark reality. Not all countries are on a level playing field with a resilient Internet infrastructure—one that maintains an acceptable level of service in the face of faults and challenges.
Many low-income countries usually have under-provisioned networks and cable infrastructure, or they lack redundant interconnection systems. In these countries (or regions), the likelihood of Internet outages occurring is much higher than in other countries. To help support the development of policies and infrastructure to improve Internet resilience at the local, regional, and global level, we’ve launched a new section on our Internet measurement platform, Pulse, to track resiliency metrics.
What We’re Measuring
- Infrastructure: The existence and availability of the physical infrastructure that provides Internet connectivity
- Performance: The ability of the network to provide end users with seamless and reliable access to Internet services
- Security: The ability of the network to resist intentional or unintentional disruptions through the adoption of security technologies and best practices
- Market Readiness: The ability of the market to self-regulate and provide affordable prices to end users by maintaining a diverse and competitive market
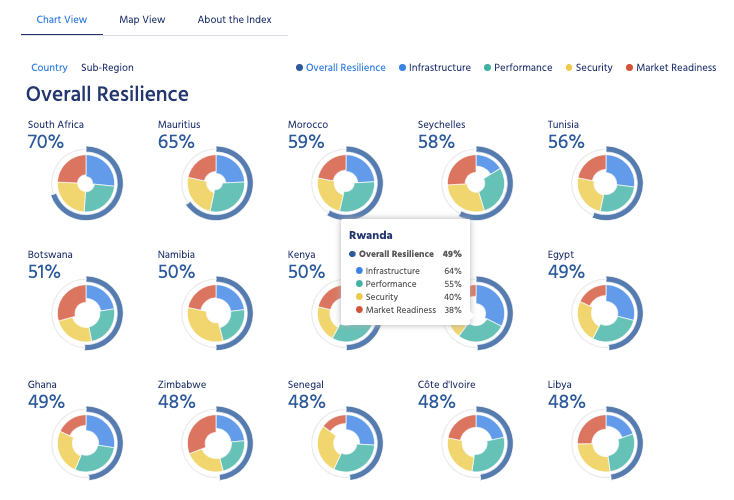
How We’re Measuring Resilience
The new Internet Resilience focus area is based on the framework outlined in the Measuring Internet Resilience in Africa (MIRA) project overview, a joint initiative of the Internet Society and AFRINIC, the Regional Internet Registry for Africa. One of the main objectives of the MIRA project is to be able to measure, as accurately as possible, the robustness of the Internet ecosystem in a country.
This is not an easy task. There are several building blocks that underpin this complex ecosystem. Additionally, the Internet landscape differs from country to country. To be able to objectively compare countries to one another, we need an objective set of metrics that we can use as a common ground.
To grasp the multi-faceted nature of the Internet we’ve built an index that gives an estimate of the overall Internet resilience of a country. This estimate, or score, is called the Internet Society Internet Resilience Index.
The Internet Society Resilience Index (IRI)
The IRI is built around the four measurement pillars outlined above: Infrastructure, Performance, Security, and Market Readiness.
Each of these four pillars represents core aspects of the Internet. Without them, the Internet wouldn’t be able to operate. The pillars themselves are made up of a series of indicators that provide empirical information about the state of the Internet at country level.
| Pillars | Dimensions | Indicators |
| Infrastructure | Cable ecosystem Mobile connectivity Enabling infrastructure | Exit points per 1M 10km fiber reach Network coverage Spectrum allocation Number of IXPs per 1M Power availability Data centers per 1M |
| Performance | Fixed networks Mobile networks | Latency Upload Download |
| Enabling Technologies and Security | Enabling technologies DNS ecosystem Routing hygiene Security threat | IPv6 adoption HTTPS adoption DNSSEC validation DNSSEC adoption MANRS score Secure Internet servers Global Cybersecurity Index DDOS potential Spam infections |
| Market Readiness | Market structure Traffic localization | Affordability % of GNI Market concentration (HHI) AS hegemony (GINI) Peering efficiency Domain count per 1M Local content E-Government Index |
Data Sources and Weighting
The data from the indicators are collected from various sources, including the World Bank, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Packet Clearing House (PCH), Mozilla, the Internet Society, Spamhaus, and the Asia Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC). We use a weighted sum formula to calculate the final index.
What’s Next?
The initial focal point of the focus area is on tracking Internet resilience in Africa. We want to test and fine tune the IRI methodology before rolling it out for other regions. No model is perfect, and we are looking at improving on it by collecting additional information and datasets over the coming months. Going forward, we’ll incorporate datasets from the Internet Shutdowns focus area, and from Keeping Traffic Local and Centralization, two new Pulse focus areas that are under development.
We Want to Hear From You
We’d like to hear your views on the new Internet Resilience focus area and on the Internet Resilience Index Methodology. Please let us know what you think by contacting us at pulse@isoc.org.

